El futuro está en el alquiler asequible
El futuro está en el alquiler asequible
Historia de nuestras formas de tenencia
Breve historia de nuestra forma de regular y desarrollar vivienda
Desde la segunda mitad del siglo XX la preponderancia de una u otra forma de tenencia ha venido marcada en las recientes décadas por la coyuntura, los ciclos económicos y la política de vivienda.
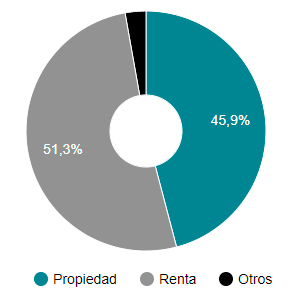
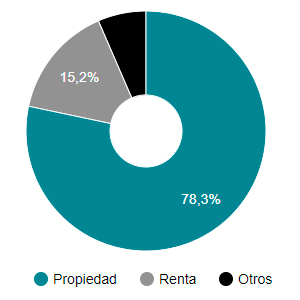
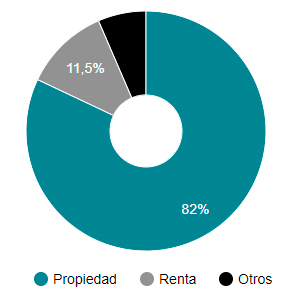
Censo 1950
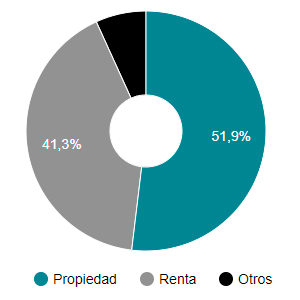
Censo 1960
Censo 1970
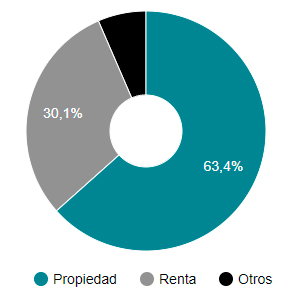
Censo 1981
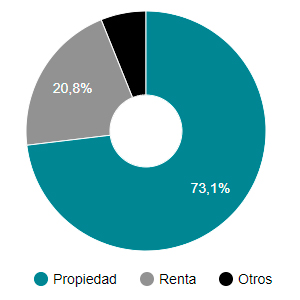
Censo 1991
Censo 2001
Fte: INE Censos de población y vivienda
Años 50
Se revelaba una preponderancia de la tenencia del alquiler, tras la Guerra Civil, el precario estado del parque inmobiliario español conllevó la generalización del alquiler, con una legislación, la LAU de 1964, muy orientada a la protección del inquilino ( derecho a prórrogas forzosas, incremento de la renta muy controlado).
Años 60-70
La LAU de 1964 y la nueva Ley de Propiedad Horizontal –PH- ( Ley 49/1960 hoy en vigor) junto a la bonanza económica de los años 60 supusieron un punto de inflexión y la forma de tenencia más popular pasó a ser el dominio. La PH colmó las aspiraciones de propiedad de una generación de españoles que se abría al mundo , la clase media se había creado, la PH como modo de organizar un multi-unit building les atribuía más o menos facultades dominicales dependiendo de si trataba de un elemento privativo o de uso común.
Años 80-90
La propiedad se vio impulsada por una normativa muy completa en relación con el sistema de crédito territorial, desde la Ley Hipotecaria de 1861 y la creación del Banco Hipotecario de España en 1872, hasta la liberalización del mercado hipotecario por LMH 1981 que creo un sistema bancario y de cajas de ahorro para desarrollar el préstamo hipotecario.
El alquiler iba decayendo por falta de medidas de incentivo y normativas, ni siquiera el Decreto Boyer RDL 2/1985 consiguió el relanzamiento del alquiler como alternativa, tampoco la vigente LAU 1994 teóricamente más equitativa al determinar derechos y obligaciones para ambas partes.
La era del 2000
Hoy y tras la nueva fallida reforma del 2013 de la LAU y tras 13 años de crisis de vivienda el arredramiento libre sigue siendo objetivamente inasequible para muchas familias, España cuenta con un mercado infradesarrollado, invertebrado, y poco profesionalizado, la escasez y menor calidad de oferta de viviendas en alquiler ha provocado una desviación hacia la propiedad, coadyuvada por la falta de presupuesto y legislación estable en políticas públicas de vivienda para el alquiler.
Los próximos años 20-30
Durante las próximas décadas tenderemos hacia una profesionalización del sector del alquiler, la legislación favorable a la vivienda de alquiler asequible será la norma general y tenderá a ser estable en el tiempo, como avanzan numerosos documentos estratégicos internacionales. Algunas decisiones políticas como la anulación de deducción por nuevas compras de vivienda (2012) y el incremento del IVA ya han tenido un impacto positivo en el incremento del alquiler. La implantación entre 2008 y 2012 de la Renta Básica de Emancipación para jóvenes entre 25 y 29 años de edad fue la primera medida política que promovía principalmente el alquiler y que rompía el antiguo paradigma de apoyo público a la propiedad.
Las formas de tenencia no deben comportar prematuros e inciertos compromisos financieros y deben dar suficiente estabilidad y seguridad temporal hasta que se desee/puedan tomar decisiones de compromisos financieros a largo plazo.